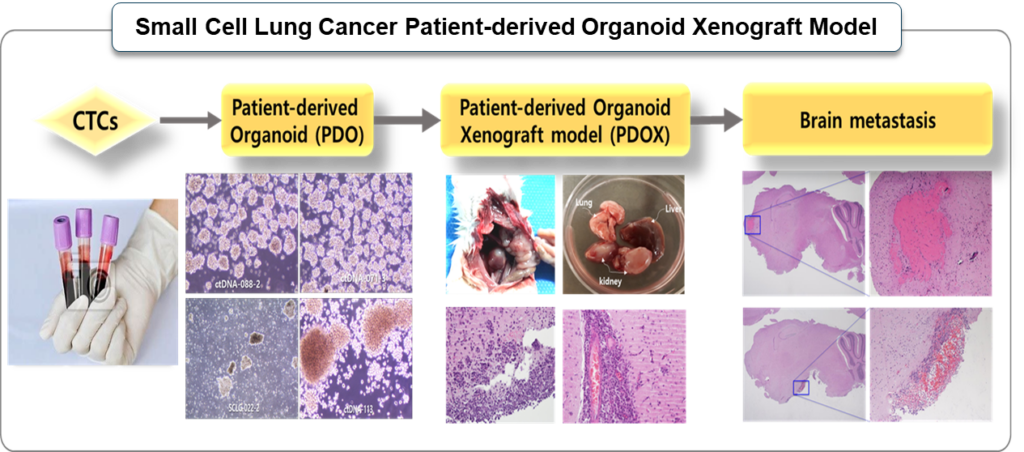
Patient-derived Circulating Tumor Microemboli Organoid Xenograft Model
The use of circulating tumor Microemboli (CTM) with PDOX models offers an innovative approach for studying metastasis and tailoring personalized therapies for metastatic cancers. By retaining the metastatic potential and microenvironment of CTM clusters, these models provide a platform for drug testing, biomarker discovery, and understanding resistance mechanisms.
– Personalized Cancer Therapy: Testing drug sensitivity and resistance in metastatic settings to tailor treatments for patients.
– Metastasis Mechanism Studies: Understanding how CTM clusters drive metastasis and interact with the tumor microenvironment (TME).
– Immunotherapy Development: Evaluating immune checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cells, and tumor-immune interactions.
Biomarker Discovery: Identifying biomarkers for metastasis, drug resistance, and therapy response.
– Anti-Metastatic Drug Testing: Developing therapies that target CTM clusters, disrupt their survival mechanisms, and prevent metastasis.
– Site-Specific Research: Mimicking metastatic growth in specific organs to study site-specific therapy responses.
Advantages of PDOX model using CTM organoid.
– CTM clusters retain TME components, enabling realistic metastatic modeling.
– Non-invasive CTM sampling via liquid biopsy makes this method accessible for patients.
– The model provides high predictive accuracy for drug efficacy.